|
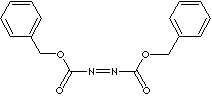
DIBENZYL AZODICARBOXYLATE |
| Phenylmethyl N-(phenylmethoxycarbonylimino)carbamate; 1,2-Diazenedicarboxylic acid 1,2-bis(phenylmethyl) ester; DBAD; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
2449-05-0; 851393-06-1 |
|
EINECS RN |
219-508-0 |
|
FORMULA |
C6H5CH2OCON=NCOOCH2C6H5 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
298.29 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow to orange waxy solid |
|
MELTING POINT |
43 - 47 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble |
|
pH |
6-8 (20% aq slurry) |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
110 C |
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. May decompose upon hearting |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Alcohols, oxidizing agents, strong bases. strong acids. heavy metals. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, Nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen gas. |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Flammable solid. Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. |
|
EYE |
Causes eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
Causes skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May cause irritation of the digestive tract. May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
Causes respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if inhaled. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XI |
|
RISK PHRASES |
36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26 |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Mitsunobu Reaction allows the conversion of primary and secondary alcohols to esters, phenyl ethers, thioethers and various other compounds. The nucleophile employed should be acidic, since one of the reagents (DEAD, diethylazodicarboxylate) must be protonated during the course of the reaction to prevent from side reactions. (source: http://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/mitsunobu-reaction.shtm) The Mitsunobu reaction is a unique dehydration-condensation reaction between alcohols and various nucleophiles using the redox system comprised of diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) and triphenylphosphine (TPP).The reactions proceed under mild conditions, and a wide variety of compounds can be used as nucleophiles, for example, carboxylic acids, active methylenes, imides, thiols, etc. The reaction between secondary alcohols and nucleophiles yields products with Walden inversion. The Mitsunobu reaction has been used widely in organic synthesis. Due to its utility, efforts have been made to expand application of the Mitsunobu reaction, and modified reactions have been reported. For example, by using azodicarboxamides instead of azodicarboxylates the Mitsunobu reaction is being applied to weak-acidity nucleophiles with a higher pKa value. Methods have also been reported for the easy removal of phosphine oxide, a reaction by-product, by utilizing phosphines which have an intramolecular basic component and diphenylphosphino polystyrene resin. (source: http://www.tci-asiapacific.com/product/synthetic-chem/S004.shtml) The Mitsunobu reaction has proven to be a useful, diverse and practical method for C-O, C-N, C-C and C-X bond formation, among other uses. Its mild reaction conditions and excellent stereoselectivity make it an excellent reaction that serves its purpose well. It will no doubt continue to be an important synthetic tool for the practicing organic chemist.(source: http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/organic/studsemin/jantzi/jantzi-abs.pdf) CARBOXYLATE-N=N-CARBOXYLATE Products
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to orange waxy solid |
| ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
43 - 47 C |